IoT — Building an automated greenhouse Pt. III
Author
KalleDate Published

This is the last session and finishes the greenhouse project. The most parts are already done, but one important part is still missing. The application should send a message whenever the plants run dry. To do so you can use the google cloud functions integrated in firebase.
The finished code can be cloned from this git repository: greenhouse
Serverless Code
To add cloud functions to your project you can init a project in the functions directory with the command firebase init. This project has a main index.js file and every exported function (exports.functionName) is deployed as a firebase function.
The firebase-functions package provides many helper functions for example to subscribe to changes in the firestore database. With this you can trigger a cloud function call whenever a new sensor value is created in the database:
To learn more take a look in the functions/index.js file from the greenhouse repository
Emails are send with the package nodemailer, it provides a simple API to use your gmail account as a sender.
Device Code
The code running on the Raspberry Pi got some changes since the last session, the default interval to read the sensor values got increased from 5 minutes to 30 minutes to reduce some noise in the diagrams. And to reduce the wear on the soil sensors the current is only set on them during the measure time. When those sensors are embedded in soil and under constant voltage the corrosion is very strong. So also the wiring changed a bit:
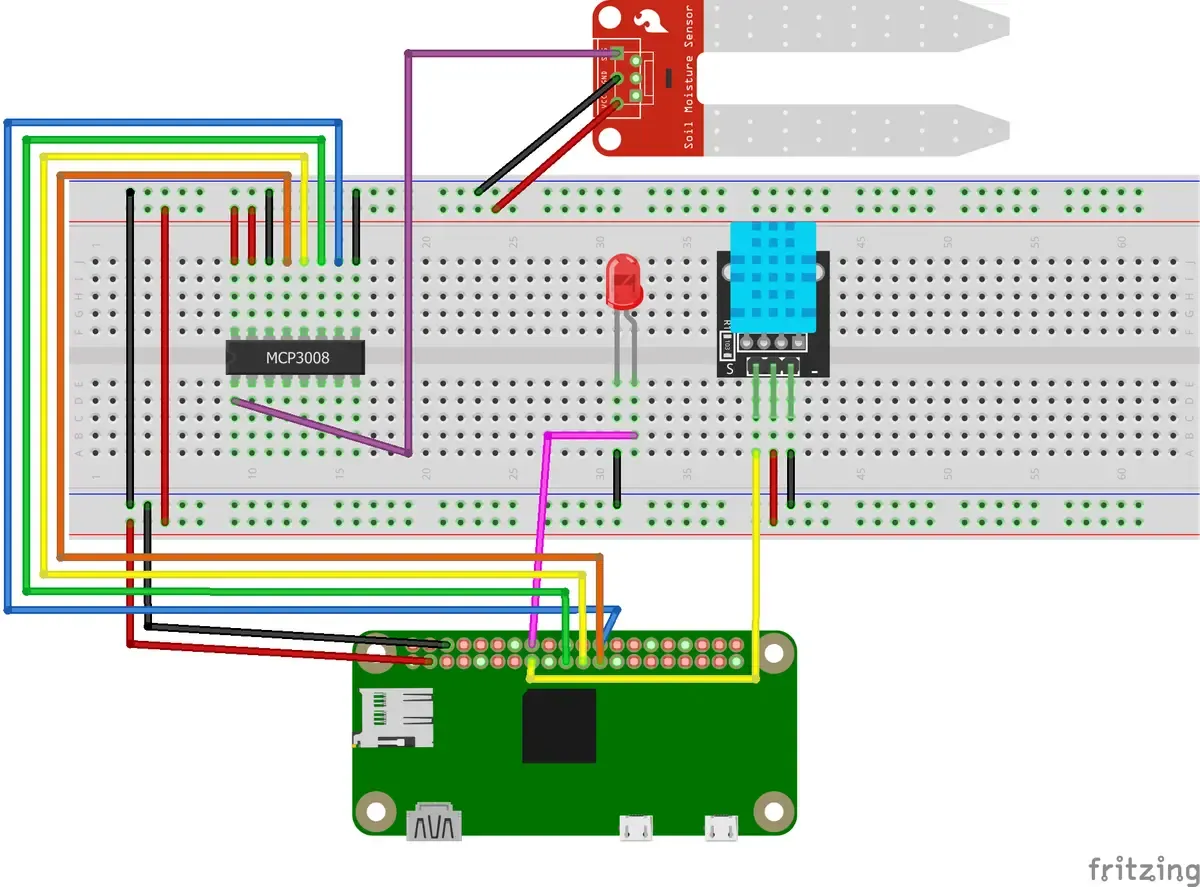
The program is located in the device/index.js file. It can be started with 2 arguments, the interval in milliseconds (-interval 60000 or --verbose 60000) in which the sensors should trigger and a verbose (-v or --verbose) flag for more logging. The default interval is 1800000 which is equivalent to 30 minutes.
Hint: it is useful to configure the node.js program as a system service so it starts automatically on startup. You can follow this nodesource tutorial
UI Code
The UI code was not changed till the last session, it is the main project in the greenhouse repository, react based and enables the user to see the current sensor states and control the reference value for dry soil.
Open ToDos to get started with your own application
- clone the repository
git clone git@github.com:kaoDev/greenhouse.git
- install firebase-tools:
npm install -g firebase-tools
- login with the firebase tools
firebase login
- connect to an existing firebase project
firebase use --add
- change firebase API keys and URLs to use your own project
This application uses an gmail account to send emails to listed users in the users collection when the soil gets dry. So you need to use an existing account or create a new one. To enable the cloud functions to send emails you must set 2 environment variables for firebase:
To deploy the application start with building the UI app, then run the firebase deploy command:
Tasks
- configure the greenhouse application and connect it with your greenhouse
- plant some seeds
- take care of the young sprouts
IoT — Building an automated greenhouse Pt. II
Continue building an automated greenhouse by adding an interface to configure soil moisture reference values and implement authentication with Firebase. This guide explains protecting database access, setting up user authentication, and updating sensor data references in Firestore.
IoT — Building an automated greenhouse Pt. I
Start building an automated greenhouse using a Raspberry Pi, sensors, and an analog-digital converter. This guide covers setting up the hardware, enabling SPI, connecting a soil moisture sensor, and writing a Node.js program to read and send sensor data to the cloud.
IoT — Data visualization
Learn to visualize IoT data by setting up Firebase and using Recharts to create dynamic charts. This guide covers connecting to Firestore, querying sensor data, and displaying it in a React app with interactive graphs.
IoT — going serverless
Explore the benefits of serverless architecture for IoT projects, focusing on using Firebase for real-time data management and deployment. This guide covers setting up Firebase, authenticating with Google, and migrating from traditional storage solutions to a serverless approach for efficient, scalable applications.
IoT — Internet of things and the cloud
Discover how IoT leverages cloud computing to manage and process data from connected devices. This post covers setting up a Node.js app on Heroku, using Git for deployment, and integrating MQTT for real-time data synchronization.
IoT — Communication protocols
Explore the various communication protocols used in IoT, focusing on MQTT for efficient machine-to-machine communication. This guide explains MQTT's lightweight binary protocol, its publish/subscribe model, and how to implement it using a message broker and Node.js.
IoT — Reading and sending sensor data
Learn how to read and send sensor data using a Raspberry Pi and a DHT11 sensor. This guide covers setting up the sensor, installing necessary libraries, and creating a Node.js application to collect and transmit temperature and humidity data to a server.
IoT — Setup and first steps with the Raspberry Pi Zero
Set up and start using the Raspberry Pi Zero, including preparing the operating system, enabling WiFi and SSH, and finding the device on your network. Learn to install Node.js and create a simple project to make an LED blink using JavaScript.
IoT — What is the Internet of Things?
Explore the Internet of Things (IoT), a vast network connecting edge devices, servers, and platforms for data collection and analysis. This post covers the basics, from embedded programs on hardware like Raspberry Pi to cloud-based machine learning, making IoT accessible for beginners and professionals alike.
Mailing List
If you want to receive updates on new posts, leave your email below.